| Features |
Starter
€ 59.00
/ month
billed annually |
Professional
€ 249.00
/ month
billed annually |
|---|---|---|
Features |
||
|
MEP Model Creation (Ventilation) For example:
|
Yes | Yes |
|
Concept in Early Design Phases For example:
|
Yes | Yes |
|
Collaboration Tools For example:
|
Yes | Yes |
|
View Creator and View Control For example:
|
Yes | Yes |
|
Storey Table For example:
|
Yes | Yes |
|
Visibility Control For example:
|
Yes | Yes |
|
Task Management For example:
|
Yes | Yes |
|
Family and Library Manager For example:
|
Yes | Yes |
|
Industry Families via CAD Browser For example:
|
Yes | Yes |
|
Parameter Manager and Classification Tool For example:
|
Yes | Yes |
|
Collision Checker For example:
|
Yes | Yes |
|
Automatic Detection of the Air Duct Network For example:
|
No | Yes |
|
Air Duct Network Calculation with Redimensioning For example:
|
No | Yes |
|
Flow mechanical Balancing of complex Systems including Sound Level Calculation For example:
|
No | Yes |
|
Bill of Quantities including Article Numbers For example:
|
No | Yes |
|
Free Access to Online Tutorials
|
Yes | Yes |
Ventilation Solutions for Revit
Editions
Videos
Description
LINEAR workflow for ventilation design with Autodesk Revit
Concept phase
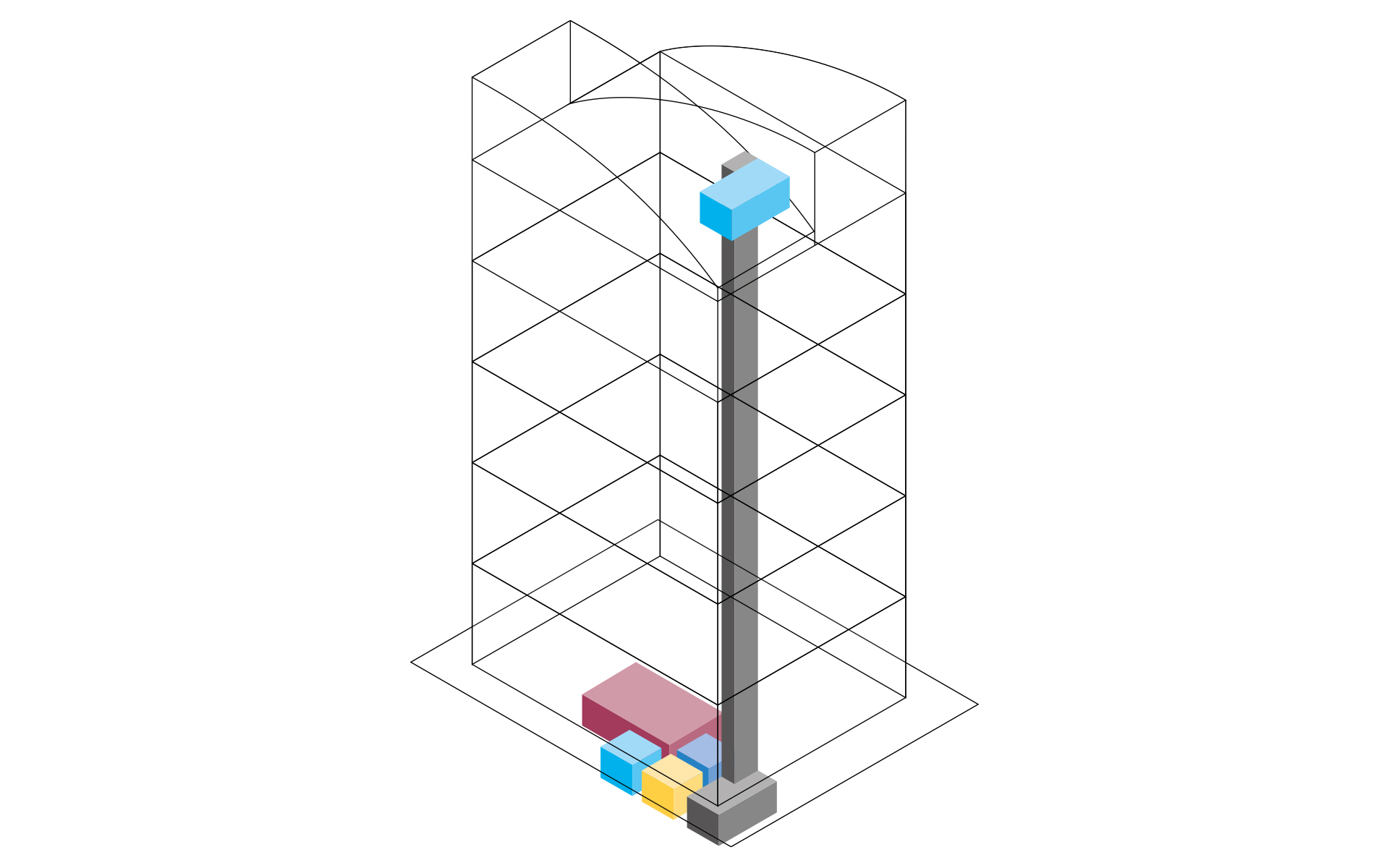

Input: Concept structure of the architecture with rooms, floors and functional areas
Output: Located space requirements for technical rooms and pipeline corridors
Work steps:
- Workflow for a collaborative early design phase planning
- Creation of a concept design on the basis of the requirements planning
- Conceptual space design (Provision for spaces)
- Localization and pre-dimensioning of technical equipment rooms
- Localization and pre-dimensioning of the pipeline corridors
- Cross section editor for the pipeline corridor concept
- Generate pipe and duct elements from corridor concept
Building model as basis for design
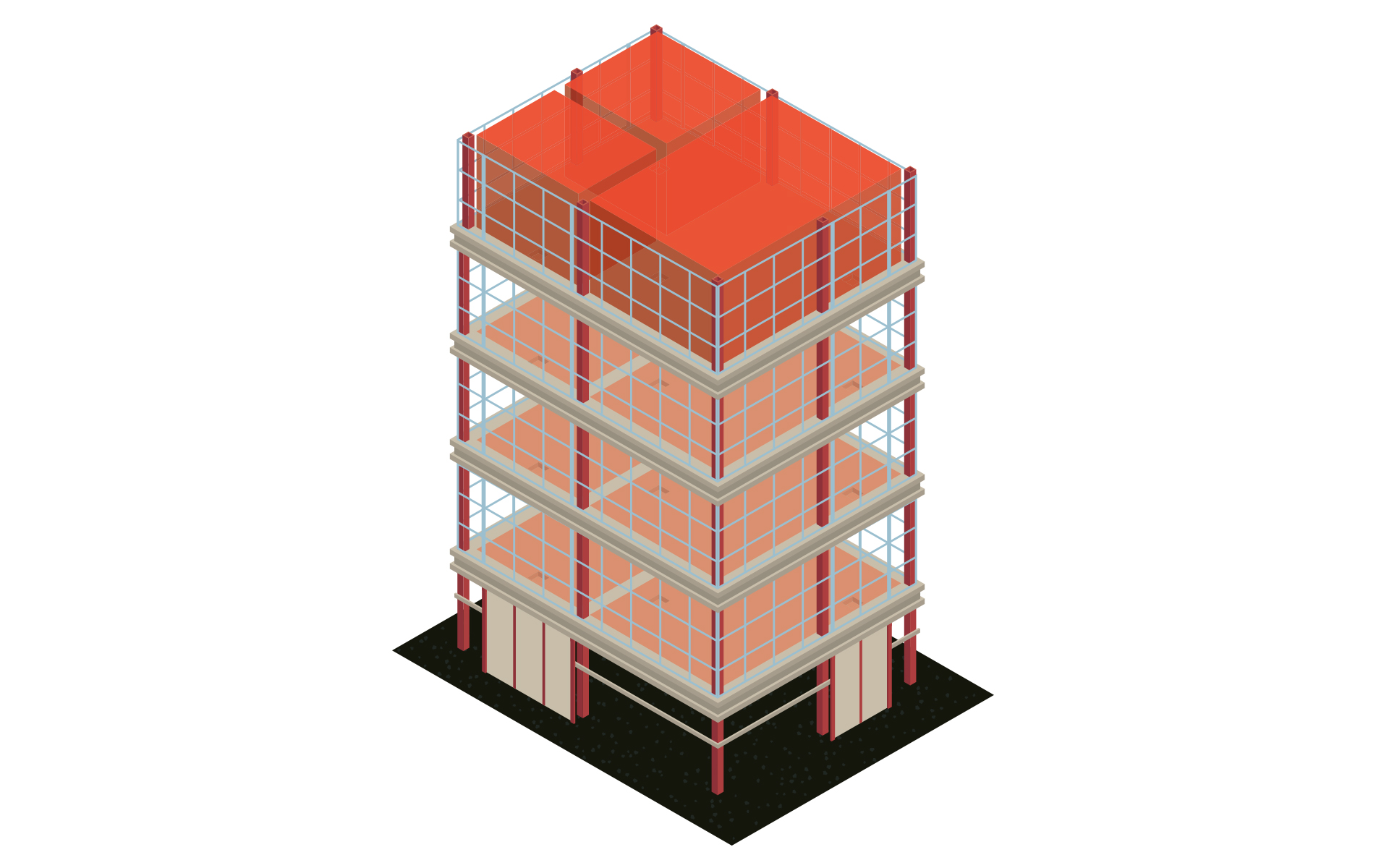

Input: Architecture model or plan
Output: Model for further MEP design including levels, zones & MEP rooms
Work steps:
- Easy creation of the MEP model based on the architecture
- Zoning and creation of MEP spaces
- Enrichment of the model with relevant information
- Automatic creation of views and plans
- Parameter management for the assignment of parameters used in the project
- Optional for 2D templates: Simple re-entry of the building in 3D
Determine volume flow rate, select outlets and configure the air handling unit
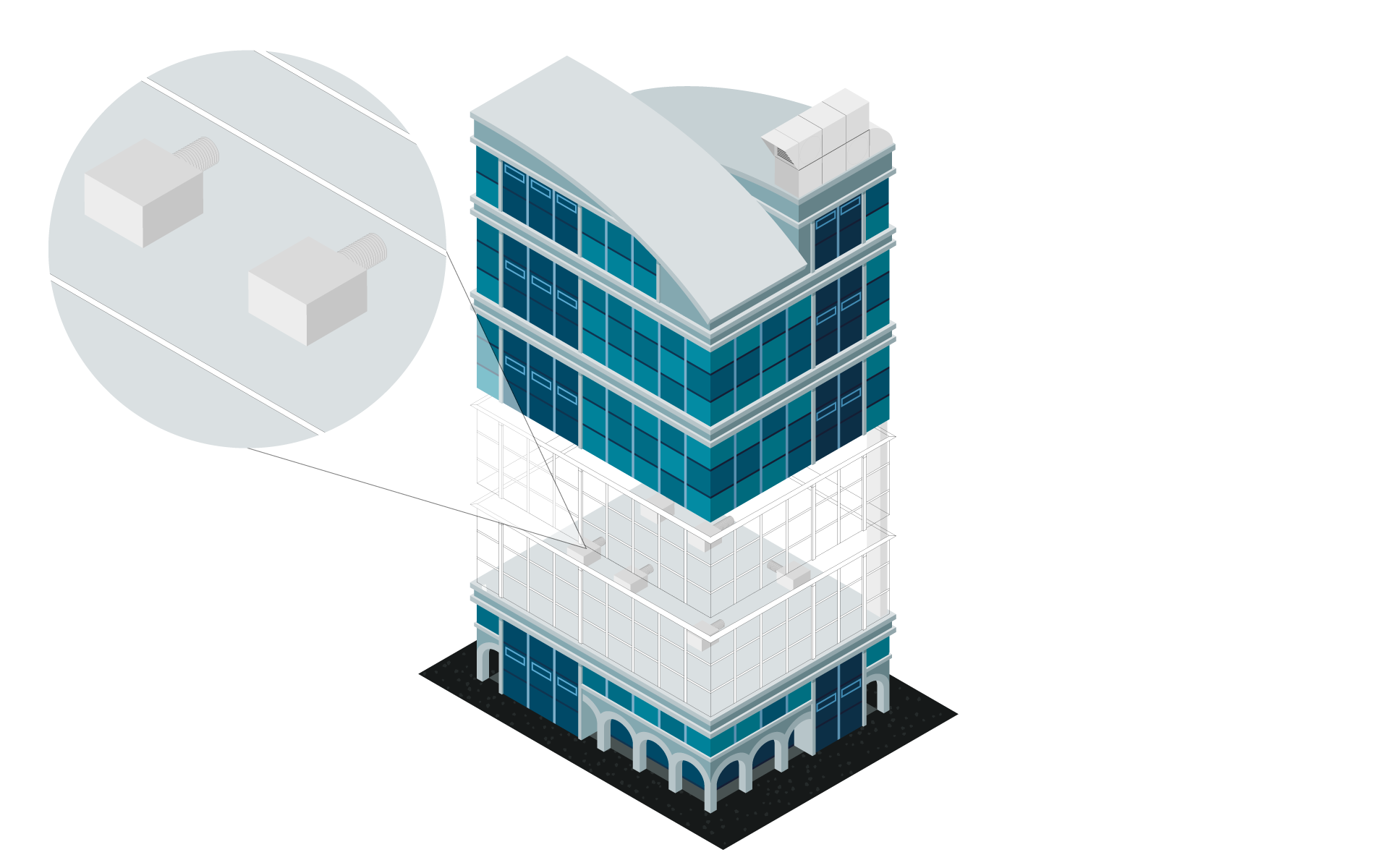


Input: Model for the MEP design including levels, zones & MEP rooms
Output: MEP model with placed outlets and ventilation unit
Work steps:
- Determination of volume flow rates room by room
- Selecting the type and number of outlets and place them
- Configuring and positioning of the ventilation unit (neutral or manufacturer-specific)
System creation and air duct network calculation
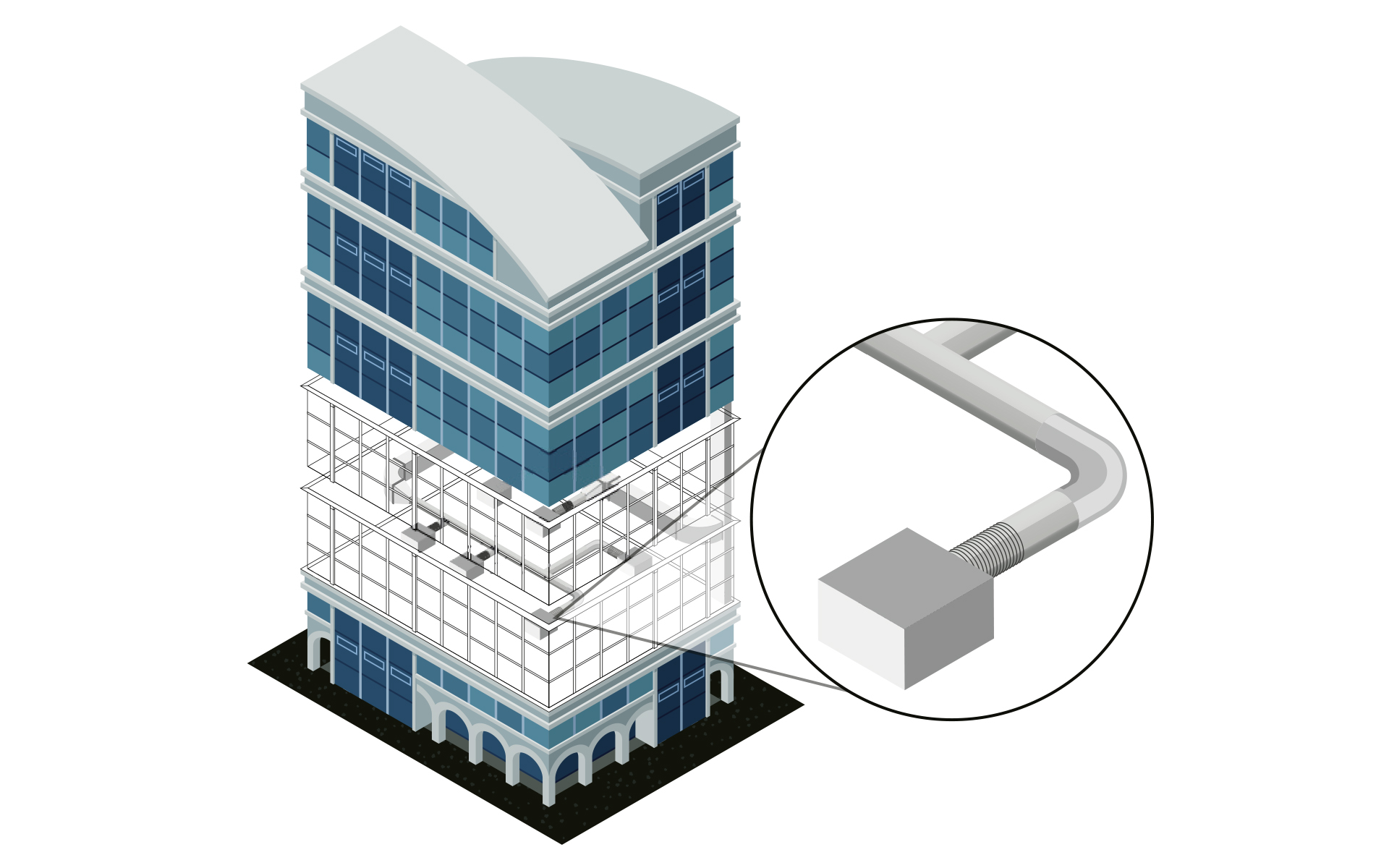

Input: MEP model with placed outlets and ventilation unit
Output: MEP model with optimized systems as well as the finished void planning
Work steps:
- Fast duct network construction round, oval and rectangular
- Automatic connection of all outlets
- Insertion of installation parts from neutral or manufacturer libraries (e.g. silencers or fire dampers)
- Air duct network calculation (pressure loss calculation, flow mechanical balancing, sound calculation)
- Support of multiple systems at the same time and many special constructions (e.g. cross-section splitting at weather grilles, several fans)
- Calculation of existing networks by fixing choosen or all dimensions
- Redimensioning of the air duct network based on the calculation
- Colored display of all results directly in the model (LINEAR data coloring)
- Void planning including coordination via BCF and IFC
- Transfer via e-klimaX directly to the air duct manufacturer
Labeling, output of model data and results

Input: Calculated and optimized air duct network
Output: Final ventilation design including model for transfer to the coordination model and calculated results incl. material lists
Work steps:
- Storage of all inputs and calculation results in the model
- Publication of selectable values as shared parameters
- Automatic labeling of the model
- Addition of own parameters and meta information
- Printout of the results in standardized forms
- Transfer of the results and the model in all relevant formats